The automobile, a marvel of engineering, has experienced transformative evolution since its inception. At the heart of this fascinating machine is the drivetrain, a crucial component responsible for the delivery of power from the engine to the wheels. Understanding the drivetrain isn’t just a journey reserved for car aficionados; it’s also essential for everyday drivers aiming to enhance their driving experience and maintain their cars effectively.
Understanding the workings of the drivetrain provides insights into the vehicle’s operational intricacies and offers drivers the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about vehicle selection and maintenance. Whether you are a seasoned car enthusiast or a daily commuter, unraveling the mysteries of the drivetrain can yield enriching revelations.
What Is a Drivetrain?

The drivetrain is the automotive system that connects the engine to the wheels, transferring power to enable motion. It’s like the intermediary between the engine, which generates power, and the wheels, receiving this power to propel the vehicle. It’s an indispensable part of any vehicle, ensuring the seamless functioning of different components to keep the vehicle in motion.
This system is the mechanical heart of a car, as it coordinates between the engine and the wheels, ensuring the generated power is efficiently utilized, allowing the car to move, stop, and change directions, enhancing the overall driving experience.
Components of a Drivetrain

The drivetrain comprises several crucial components, each playing a pivotal role in the car’s operation. The primary components are the transmission, driveshaft, axles, and the differential. These parts work synergistically, ensuring the seamless transmission of power from the engine to the wheels.
Transmission: This component modulates the engine’s power, enabling the driver to control the vehicle’s speed and direction.
Driveshaft: This elongated round shaft sends the rotational power (torque) from the transmission to the axles.
Axles: These structures hold the wheels in place and transfer the rotational power from the driveshaft to the wheels.
Differential: This device allocates engine power to the wheels, allowing them to rotate at different speeds, especially when cornering.
Types of Drivetrains
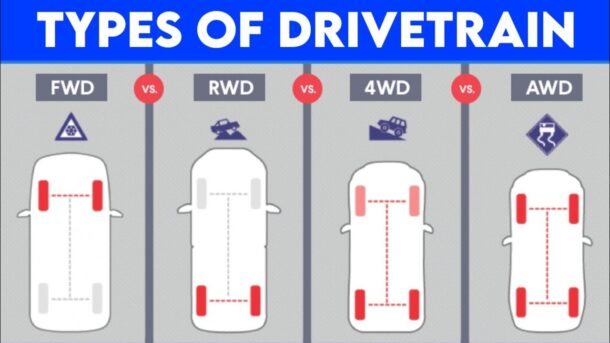
Drivetrains come in different configurations, with each serving a unique purpose. The primary types are Front-Wheel Drive (FWD), Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD), All-Wheel Drive (AWD), and Four-Wheel Drive (4WD). Each configuration impacts the vehicle’s handling, traction, and performance differently, catering to varied driving conditions and preferences.
Front-Wheel Drive (FWD): This configuration is prevalent in modern vehicles due to its compactness and efficiency. The power is channeled to the front wheels, making it suitable for regular driving conditions. Cars with FWD tend to have better fuel economy and are generally less expensive to produce.
Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD): In this setup, the power is directed to the rear wheels, providing better balance and handling at high speeds, making it a favorite for sports cars and luxury vehicles.
All-Wheel Drive (AWD): This system powers all four wheels simultaneously, enhancing traction and control, especially in unfavorable driving conditions, such as snow or mud.
Four-Wheel Drive (4WD): Similar to AWD, 4WD also powers all wheels but is more robust, catering to off-road driving and extreme terrains.
Front-Wheel Drive (FWD)
The Front-Wheel Drive system is a popular choice due to its economical and practical advantages. In FWD, the front wheels receive power and pull the car forward, offering better traction while climbing hills and enhanced stability while braking. It is inherently more straightforward, resulting in lower manufacturing costs and improved fuel efficiency.
However, FWD cars may suffer from torque steer, where uneven power delivery can cause the car to pull to one side during acceleration. FWD is common in compact and mid-size cars due to its economical benefits and adequate performance for everyday driving.
Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD)
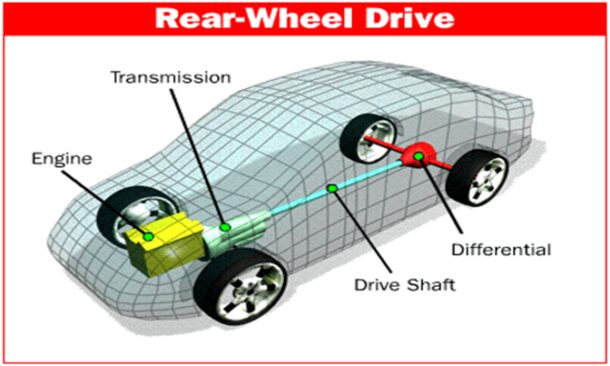
Rear-Wheel Drive cars have the drivetrain powering the rear wheels, providing a superior balance and handling, making them suitable for high-performance and luxury cars. The distribution of weight is more balanced in RWD vehicles, improving handling, especially during cornering.
However, RWD cars may have less traction on slippery surfaces and can be challenging for inexperienced drivers to handle in extreme conditions due to oversteer scenarios. Despite this, the RWD configuration is preferred for its performance benefits and enhanced driving experience.
All-Wheel Drive (AWD)
All-Wheel Drive systems deliver power to each wheel individually, adapting to changing driving conditions, providing enhanced stability, and control. AWD is beneficial in varied and unfavorable terrains and weather conditions, offering a blend of performance and safety.
The sophisticated power distribution in AWD ensures optimal traction, reducing the likelihood of the vehicle getting stuck in mud or snow. However, AWD systems can be complex and may reduce fuel efficiency due to the added weight.
Four-Wheel Drive (4WD)
Four-Wheel Drive is the go-to configuration for off-road enthusiasts, providing immense power and traction on challenging terrains. 4WD systems are robust and versatile, allowing drivers to switch between two-wheel and four-wheel drive, depending on the driving conditions.
While 4WD offers unparalleled off-road capabilities, it can be cumbersome and less fuel-efficient during regular city driving due to the added weight and complexity.
Transfer Cases and Differentials
Transfer cases and differentials are integral components of the drivetrain, enabling the distribution of power and ensuring smooth operation. The transfer case, found in 4WD and AWD systems, distributes power between the front and rear axles, allowing for balanced and controlled driving.
The differential, on the other hand, allocates power between the left and right wheels, enabling them to rotate at different speeds and ensuring smooth cornering. These components work together to provide a harmonious driving experience by balancing power distribution and enhancing maneuverability.
Transmission Types
The transmission is a pivotal component in the drivetrain, modulating power from the engine to the wheels. There are several types of transmissions, including manual, automatic, and Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT).
Manual Transmission: Requires the driver to manually select gears, offering precise control over the vehicle’s power.
Automatic Transmission: Shifts gears without driver input, providing a convenient and straightforward driving experience.
CVT: Provides a seamless range of gear ratios, ensuring optimal engine performance under different driving conditions.
Drivetrain Maintenance
Maintaining a healthy drivetrain is crucial for the longevity and performance of a vehicle. Regular inspections, timely oil changes, and addressing issues promptly can prevent extensive damage and ensure smooth operation. Common drivetrain issues include unusual noises, vibrations, and difficulty in handling, all of which require immediate attention.
Following the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule and using high-quality lubricants can significantly enhance the drivetrain’s lifespan, enabling optimal vehicle performance and reducing the risk of untimely breakdowns.



